Together with…

Introduction
There are several ways to hold Bitcoins: receive them as a payment for a product and a service, exchange FIAT currency in Bitcoin through an exchange, and be part of the Bitcoin mining process.
Mining is the extraction process that allows the introduction of new digital coins into the circulating supply. The concept behind Bitcoin is, in fact, a consensus algorithm called Proof of Work that allows the creation of new Bitcoins up to 2140, the year in which the last one will be mined.
At the date of preparation of this analysis, there are 2.5 million Bitcoins still to be mined and, at the present time, each of these Bitcoins has a value that fluctuates between 30,000 and 35,000 dollars.
How exactly does mining work?
The Blockchain is a technology composed of a chain of blocks. Each block contains information relating to all transactions carried out over a certain period of time on the entire blockchain. The new blocks are processed and generated by a “component / node” of the chain called miner, which has the task of solving a random sequence of letters and digits called ‘hash’. Each hash is unique and, by modifying even a single alphanumeric character of the sequence, an anomaly is created, immediately detectable by all the nodes of the network. This function determines, in fact, the incorruptibility and security of the entire protocol.
Any attempted fraud on the Bitcoin blockchain can therefore be easily identified, isolated and neutralized. The blockchain is administered and controlled by solving these complex mathematical operations, an activity that requires computational work called Proof of Work. Miners contribute to the maintenance of the Bitcoin blockchain by confirming each transaction and ensuring its legitimacy. In doing so, they constantly compete with each other since the resolution of the hash algorithms ensures them a compensation equal to a few units of Bitcoin.
The value of the bonus paid for the work done by the miners [1] is halved every 210,000 blocks completed: [2] this event takes place every four years and is called halving. This is another feature inherent in the protocol that ensures the cryptocurrency its great value, since bitcoin mining is not an infinite process, which makes it a scarce commodity. The activity of mining new Bitcoins has very low probability of success (just like the attempt to extract metals or precious stones). It requires great computational power due to the many attempts required to generate a valid hash sequence and, with it , a new fraction of Bitcoin.
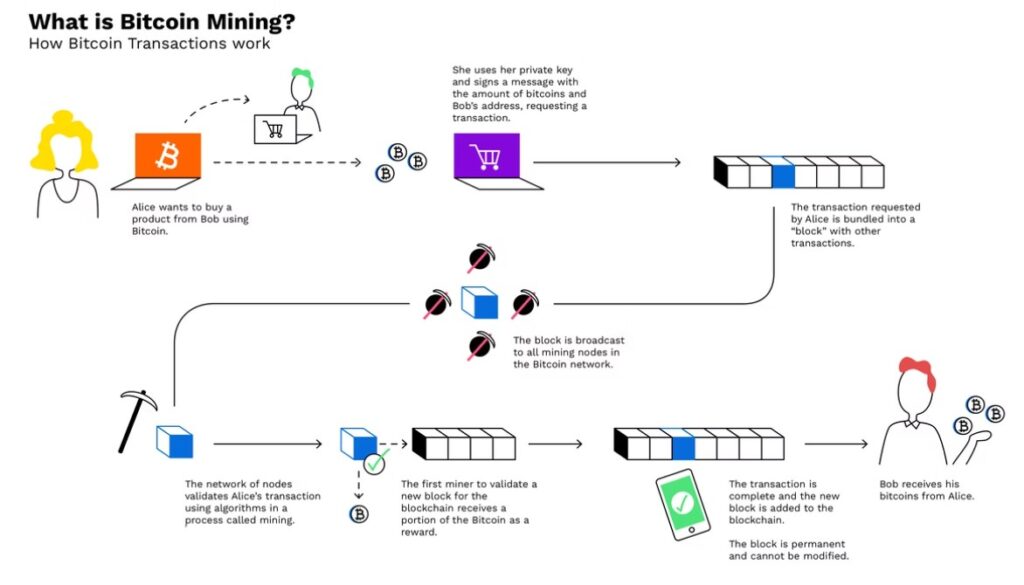
Furthermore, every 2016 exact blocks, the algorithm calculates a new value called Bitcoin Difficulty. This variable, which makes the extraction process even more complex and therefore precious, is based on the computation time of the mining: each block, in fact, always needs about 10 minutes to be mined. If more miners are added to the bitcoin network, the speed of generating new blocks increases: the difficulty level will then be recalculated, increasing the rewards and slowing down the block creation speed again. If there are miners who do not respect the new level of mining difficulty, they will be considered fraudulent and the blocks they mined will be immediately rejected.
What is the hash rate?
The hash rate is the unit of measurement for the processing power of the Bitcoin network.
This parameter greatly affects the activity of miners: the greater the computing power of the entire Bitcoin network, the greater the difficulty of mining, which is adjusted every 2016 blocks.
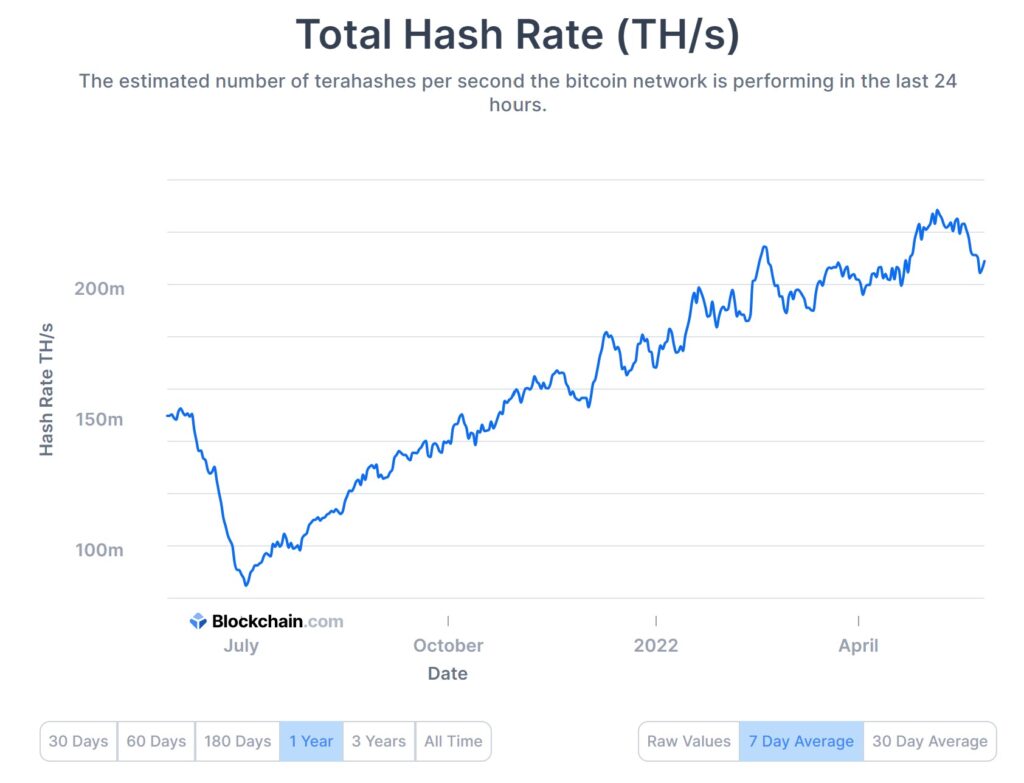
At the time of writing this analysis, the Bitcoin Hashrate is equal to 109.9m TH / s. As shown by the graph, the macro trend is in a phase of exponential growth, and is destined to increase. Even if the latest events in China have caused the value of the hash rate to drop below 100 EH / s, it still seems to be recovering. At the beginning of the Bitcoin era, cryptocurrency could be mined with simple GPUs, while at present the only possibility to mine Bitcoin is the creation of immense structures, defined as “crypto mining farms”, consisting of pools of dedicated machines called ASICs (application specific integrated circuit).
How do miners behave when Bitcoin’s price moves significantly?
One of the most debated issues in the world of Digital Assets has always been the link between Bitcoin price and Hash Rate. Specifically, one wonders if it is the first to follow the second or vice versa.
Certainly, in the face of the increase in the price of Bitcoin, the profitability for miners turns out to be higher, but the calculation complexity of the hash algorithm will also be higher. This requires more computational power and, therefore, higher investments in hardware and energy to carry out the mining activity. On the other hand, as the price of Bitcoin decreases, the profitability for miners drops significantly while the fixed costs associated with the activity remain constant, especially the cost of the energy required.
Basically, when the price of BTC increases, miners are more willing to solve the algorithmic calculation, making it more complex and difficult to access, and more blocks will be created in a period of time. From the Bitcoin investor’s point of view, the hash rate can be considered an interesting metric, as it anticipates the amount of investments that miners will have to make to remain competitive and with them the potential level of Bitcoin price growth on average term.
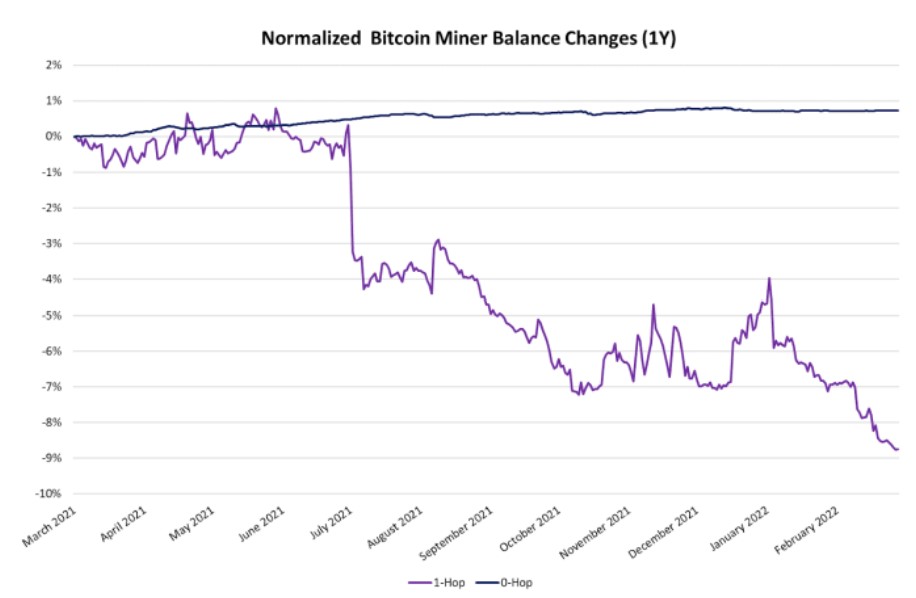
Interesting, in this sense, is what happened on the 11th June 2021 when the last two blocks in the Bitcoin blockchain, in particular the number 687142 and 687143, were created with an interval of about 2 hours (compared to the canonical 10 minutes ). The cause is the sudden collapse of the hashrate which in turn was caused by the blockade of the mining farm in China.
In any case, it must be said that this is not a recurring problem and, above all, it is not lasting over time, because at the next adjustment of the network difficulty, it will realign itself, reporting the creation of new blocks with intervals of about 10 minutes.




