Crypto Market, no easy game
The great innovation of the crypto world, initially introduced by its most important representative Bitcoin, was the creation of decentralized trading systems, capable of assigning unique values to all transactions on the blockchain.
New important markets and industries are emerging from this disruptive technology. In recent years, one in particular, Decentralized Finance aKa DeFi, has recorded unimaginable volumes and growth speeds.
However, according to the data, in this early stage the cryptocurrency market was characterized by a very high volatility, this feature has allowed the most advanced investors to carry out incredible speculative operations, with all the risks and consequences that derive from them and which the entire system often pays dearly for.
Also, in the beginning there was the idea that the cryptoasset market was totally unrelated to traditional financial markets.
This belief, which has recently proved to be false, has contributed to the increase in trading volumes and the growth of global capitalization, although at the moment, the market is still highly inefficient and full of “bull traps” for non-professional investors.
In summary, while full of opportunities, the cryptocurrency market has been subject to periods of strong growth followed by dramatic downturns. The latest example was the steep decline in the price of Bitcoin in mid-2022 from its peak of $69,000 in November 2021.
Furthermore, the recent bankruptcies of the year 2022; centralized exchange FTX, Alameda Research, the hedge fund 3AC and the Terra/Luna protocol, suggest the need for a much more professional and supervised approach to these markets than what has happened since Now.
The DeFi paradox. Is Decentralization the key?
The fall of FTX was a shocking event for the entire market, not only because of the speed with which a $32 billion company disappeared in 10 days but because it highlighted, in a cold and crude way the need to quickly develop a regulatory framework to safeguard the growth of the entire industry.
What happened was evidence of a strong lack of transparency and supposed fraud that made $10 billion like simply disappear.
For sure, without centralized exchanges like FTX/Binance/Coinbase/Kraken, there are no mainstream fiat on-ramps to crypto, but a comparison with decentralised protocols (where code is law, no humans between) is unavoidable: smart contracts and the specific structure of the blockchain guarantee transparency and ensure immunity from mismanagement by the managers.
Automation, code verification and on-chain analysis in DeFi allow for better risk management and there are no unexplained flaws in the system, which can happen in human-managed systems.
In fact, the repercussions on decentralized protocols, that we are seeing in these last weeks, are derived from the errors and human frauds that occurred in CeFi exchanges; for example, the Solana ecosystem has been severely affected in recent weeks, but not because of technical problems within the protocol, rather because Sam Bankman-Fried, the founder of FTX and his hedge fund Alameda Research, were among Solana’s most important investors.
The fear of the sale of 1 billion SOL (Solana Token) by Alameda has led to a massive sell-off capable of putting the entire blockchain at risk. Fortunately, Solana proved to be much stronger than expected, technically stable and functional, which allowed its survival.
Thus, the main cause of FTX’s failure stems from the centralisation aspects of the system, even though the main alarm at blockchain technology is often associated with the decentralised finance aspects, which are more innovative and therefore less well-known.
Hacking in the DeFi Space
In the Decentralized Finance world transactions are executed automatically and smart contracts, based on blockchain, allow people to trade directly with each other without the oversight of big banks (or any banks).
DeFi and its openness are so powerful but bring with them some downsides: the easier accessibility, the chance for anonymity and the relative immaturity of the underlying technology have allowed hackers to steal users’ funds; also, the deep pools of liquidity have allowed for launder proceeds of crime such as ransomware and fraud.
In 2021, for instance, more than $10 billion was lost to DeFi scams. However, frauds and scams are not uncommon even in regulated markets, such as stock markets.
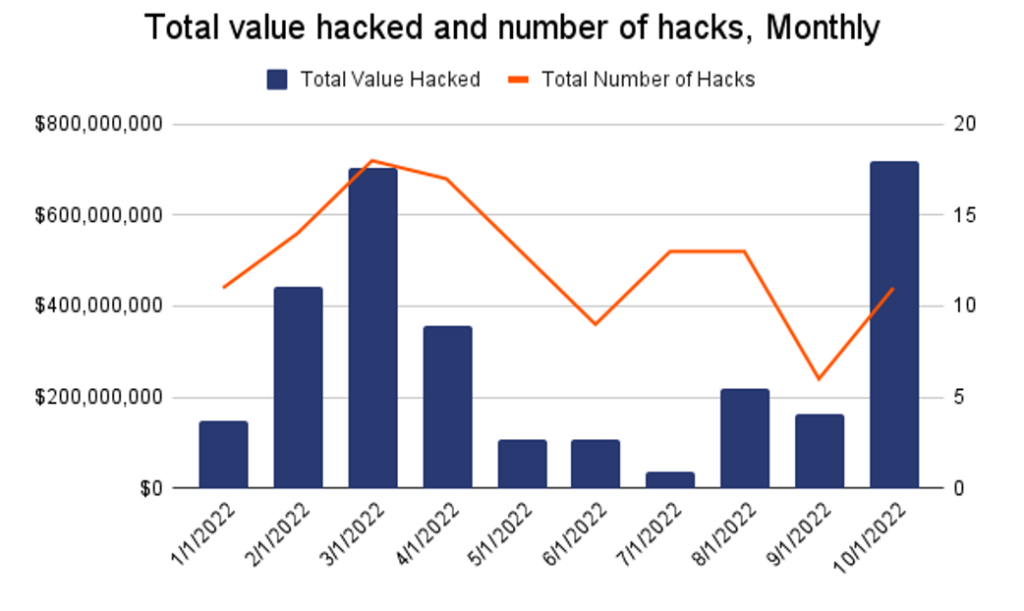
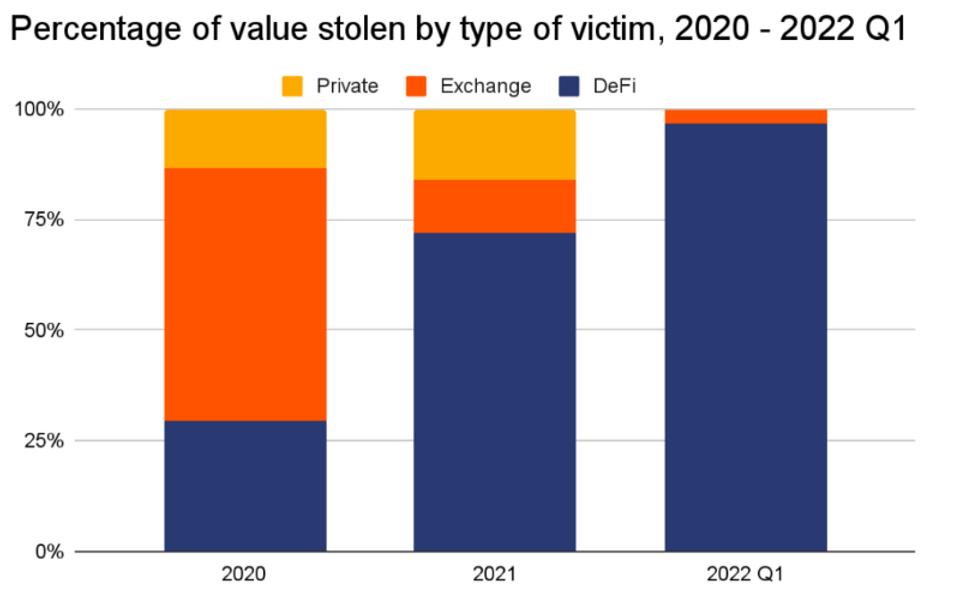
Despite the constant evolution and maturation of blockchain technology and the crypto market, 167 attacks on Decentralized Finance protocols, 123 security attacks, and 74 fraudulent schemes over the last 11 years (January 2011-October 2022) have so far resulted in the stealing of approximately USD $14.5+ billion worth of cryptocurrency assets in total.
Focusing on this last year, 2022, the total value of stolen funds surged to almost $3B, that’s nearly double the $1.5B hackers took in 2021 and nearly 12 times the 2020 total. A pick of hacking was verified in the month of March, but then the month of October has been particularly significant reaching a record of about $760M in exploits in October.
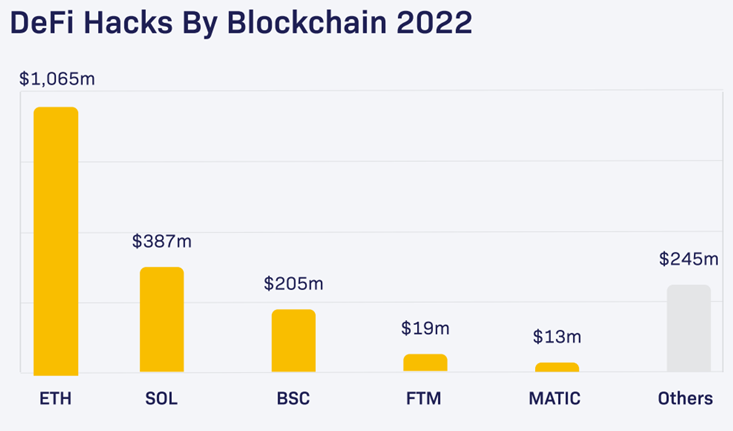
As shown by this ranking, Solana has been the second most hacked blockchain during 2022.
Beyond illegal hacks, there are various types of fraudulent schemes that bad actors have used to gain value from unsuspecting victims, including, for example, exit scams and Ponzi schemes.
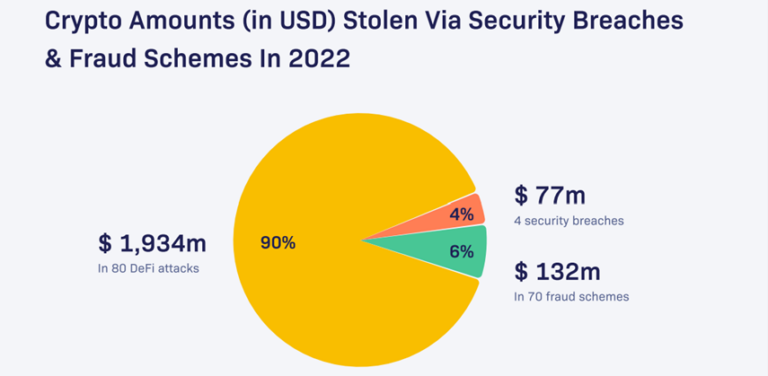
The total number of cases of illegal activity in the first half of 2022 has already reached 154, with most cases, 80, being connected to the hacking of DeFi projects.
The danger of hacking is complex to deal with, and for this purpose, new companies have been born with the aim of protecting against these crimes, and others have come up with alternative solutions to work around the problem, such as the so-called Bug Bounty.
Bug bounty programs constitute an important Web3 Security Revolution: they offer monetary rewards to ethical hackers for successfully discovering and reporting a vulnerability or bug to the application’s developer, this allows companies to leverage the hacker community to improve their systems’ security posture over time.
There are several examples of cybersecurity systems that have been gaining popularity lately in light of recent problems.
Are there any strategies to improve the current situation? We believe YES: Hacken
Hacken is a cybersecurity auditor who provides cybersecurity services to clients belonging to the blockchain, DeFi, and NFT ecosystems from Europe, Asia, and North America.
The business structure developed aims to build security infrastructure for the blockchain and crypto industry, ensure protection from major cyber risks, and create awareness of the dangers of web3 assets. In doing this, Hacken proposes many services:
- Smart contract audit: identification of vulnerabilities to remove them, problem analysis and code optimisation to prevent hacks and increase audience trust.
- Blockchain control audit: securitization of the entire architecture and optimization of protocols functioning.
- Penetration Testing: testing services for simulations of real attacks.
- dApp audit: decentralized apps run on peer-to-peer networks and use code-based smart contracts, they are open-source and based on blockchains where all data are stored. dApp audit helps projects create and maintain secure integrations with blockchains and protect assets.
- Bug Bounty
- Proof of Reserves: kind of audit conducted which aims to ensure that on-chain holding of cryptocurrencies by exchanges matches up with users’ balances. This could be an effective way to build trust in the market and verify transparency.
Are there any strategies to improve the current situation? We believe YES: Elliptic
Elliptic provides blockchain analytics for cryptoasset compliance, to detect and prevent financial crime. The crypto economy is a new front that can no longer be ignored and gives rise to huge digital monetary operations, so the core mission is to secure transactions and investments. The kind of customers elliptic refers to mainly are crypto businesses, financial institutions, and governments.
In DeFi context, blockchains have become easily interconnected, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and cross-chain bridges have removed many of the barriers to the free flow of capital and this creates an occasion for hackers and abusers to launder money or commit frauds. Elliptic aims to identify these illicit users by applying multi-asset screening and cross-asset tracing.
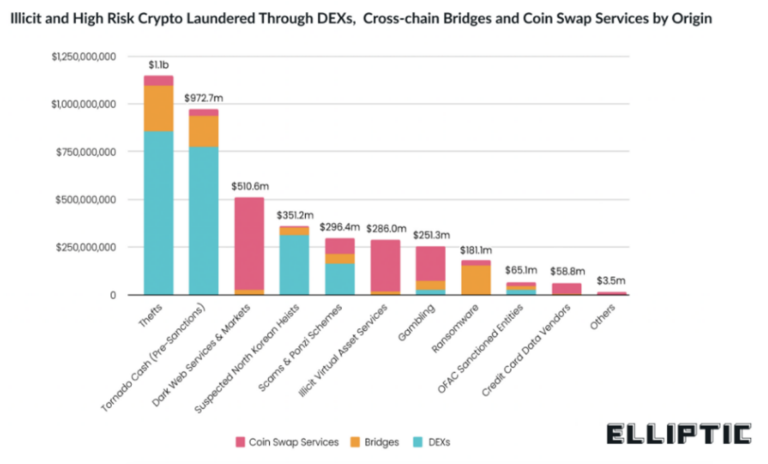
2022 has been a decisive year for the definition of a new series of blockchain analytics to interface with an ever-increasing exposure to risks. Holistic Screening is Elliptic’s response to the rapidly changing state of crypto crime; traditional blockchain analytics solutions are no more able to investigate transactions across different blockchains and so can not view the activities of the same entity across separate chains holistically, but this is actually a very important point. Going into detail, Elliptic implements several inspection activities:
- Multi-asset screening: the screen of wallets across all assets that they have ever contained for incoming and outgoing exposure to risk.
- Cross-asset tracing: the tracking of transactions involving the exchange of crypto assets on the same blockchain.
- Cross-chain tracing: the tracking of transactions across different blockchains.
The importance of data, the oracles.
Fundamental elements for the proper functioning of decentralized markets are oracles.
In DeFi, oracles are middlewares that provide blockchains access to off-chain data and services: blockchains are by nature disconnected from the outside world, but most high-quality financial market data is generated out of these environments (“off-chain”), oracles are therefore essential to instantly obtain the current or historical price of various cryptocurrencies (or real-world assets) that determine the actions undertaken inside the chains. Unsafe price oracles can cause losses, so to protect billions of dollars, it is essential they are verified.
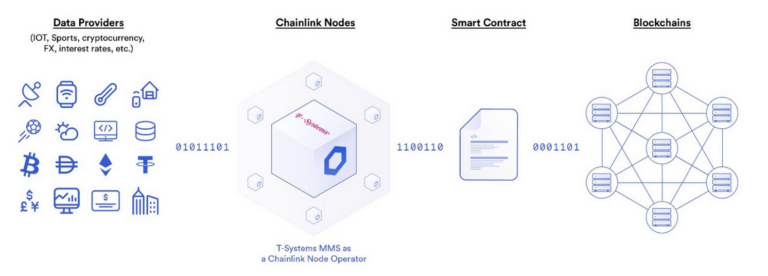
Chainlink Labs is a provider of trusted open-source blockchain oracle solutions that connect smart contracts to a wide range of off-chain data sources and calculations, such as asset prices, web APIs, IoT devices, and payment systems. The service is offered to any blockchain.
To wrap up, this is a market that needs the presence of regulation: the evolution of the DeFi system will come from the entry of regulated and supervised companies, subject to certain rules, and the presence of services capable of providing data sets and valuable information, to make investors, and consequently the market, more aware and professional. The intention will be to eliminate excessive risks and inefficiencies, so as to make this industry truly attractive to professional investors/institutions and generate prospects for organic and lasting growth.
Join ThePlatform to have full access to all analysis and content: https://www.theplatform.finance/registration/
Disclaimer: https://www.theplatform.finance/website-disclaimer/



