Together with…

Hacking in the DeFi space
In the Decentralized Finance world transactions are executed automatically and smart contracts, based on blockchain, allow people to trade directly with each other without the oversight of big banks (or any banks).
DeFi and its openness are so powerful but bring with them risks: the easier accessibility, the chance for anonymity and the relative immaturity of the underlying technology have facilitated hacking and fraud. In 2021, for instance, more than $10 billion was lost to DeFi scams. However, frauds and scams are not uncommon even in regulated markets, such as stock markets.
The crypto industry faces several risks of hacking, including:
- Phishing scams: Hackers use fake websites and emails to trick users into revealing their private keys or login credentials.
- Malware: Malicious software can infect computers and steal sensitive information, including crypto assets.
- Exchange and wallet breaches: Exchanges and wallet providers can be hacked, allowing attackers to steal large amounts of cryptocurrency.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities: Smart contracts can contain coding flaws that allow hackers to steal or manipulate assets.
Despite the evolution and maturation of blockchain technology and the crypto market, 167 attacks on Decentralized Finance protocols, 123 security attacks, and 74 fraudulent schemes over the last 11 years (January 2011-October 2022) have so far resulted in the stealing of approximately USD $14.5+ billion worth of cryptocurrency assets in total.
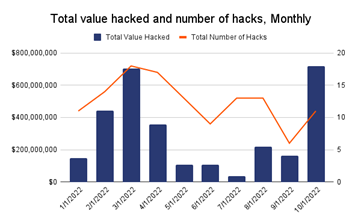
Focusing on the year 2022, the total value of stolen funds surged to almost $3B, that’s nearly double the $1.5B hackers took in 2021 and nearly 12 times the 2020 total. A pick of hacking was verified in the month of March, but then the month of October has been particularly significant reaching a record of about $760M in exploits in October. This highlights the need for increased security measures in the industry to protect against these attacks.
The evolution of Web3 industry
The Web3, or the third generation of the internet, refers to the new stage in the evolution of the internet, that aims to build a decentralized and more equitable online environment where users have more control over their data and digital assets. Unlike the first two generations of the internet, which were characterized by centralization and a focus on information access and exchange, Web3 emphasizes user control, privacy, and security.
The key driver of web3 is a decentralized technology, specifically blockchain, which is the infrastructure where applications are built; it is used to secure and verify transactions, store data, and enforce rules. Existing applications in this environment are based on Smart Contacts.
Smart Contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In this context, they play a crucial role in enabling decentralized applications (dapps) and automating processes in a secure and transparent manner. These apps run on peer-to-peer networks and use code-based smart contracts to facilitate agreements between parties without the need for pre-established trust.
Decentralized apps are fully open source, store data on an open blockchain, generate tokens, which are required for the app usage, and are awarded to users in exchange for their contributions.
The importance of smart contracts in Web3 can be attributed to the following reasons:
- Automation: they automate the execution of predefined rules and conditions, eliminating the need for intermediaries or manual processes. This helps to reduce the risk of errors and increase efficiency.
- Transparency: they are open-source and transparent, allowing anyone to verify and validate the code. This aims at increasing trust and accountability but represents one of the points that make this system sensitive to attacks.
- Programmability: smart contracts are written in code and are programmable, allowing for flexible and dynamic rules and logic. This allows for the creation of complex and customizable systems that can adapt to changing needs and requirements.
As cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology continue to gain popularity, traditional financial institutions and tech companies are exploring ways to integrate web3 technology, but the transition to this system involves hacking risks as mentioned.
Hacking risk of smart contracts
In the Web3 environment, theft is often achieved through hacking smart contracts. These contracts have certain characteristics that make them susceptible to this risk.
Firstly, smart contracts can be improperly coded and contain errors that can be potentially exploited by attackers; moreover, the code is immutable, so it is difficult to fix vulnerabilities.
Secondly, the lack of third-party oversight in the self-executing nature of smart contracts can result in undetected malicious activities. The interaction with other contracts can also introduce unexpected security risks. Furthermore, the limited computing power of the blockchain can slow down processing times and lead to further security vulnerabilities.
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to conduct thorough testing and auditing of smart contracts before deployment.
Amulet Protocol Solution
Amulet Protocol is a decentralized risk protection protocol built for the Rust-based ecosystem, starting with the Solana blockchain; it offers a variety of policies and solutions to provide safety for digital assets, for example, coverage options for smart contract risk, stablecoin de-peg, and NFT.
The vision of Amulet is to offer simple, reliable insurance for everyone in Web3.
Given that Crypto can be stolen like other assets, Amulet provides a product for that risk. Before selling a product Amulet performs a deep analysis and audit of the code of a contract and calculates a premium, based on its risk factor. Cover policies are generated and sold based on this premium.




