Together with…

Insurance: Traditional vs DeFi
In the traditional world, insurance has been provided by centralized companies that operate through traditional financial systems. On the other hand, the DeFi (decentralized finance) space has emerged as a new and innovative way of providing insurance.
Traditional insurance operates through a centralized system where insurance companies assess the risk involved in providing coverage and determine the amount of premium to be charged. Policyholders purchase insurance by paying the premium, and in the event of a covered loss, they file a claim with the insurance company for payment. Insurance companies often invest in policyholder premiums to generate additional revenue. Traditional insurance is regulated by government agencies and offers a level of stability and security. However, it can also be subject to limitations such as limited coverage, high premiums, and long claims processing times.
DeFi insurance, and in particular Crypto insurance, refers to insurance coverage for cryptocurrency-related risks; this can include coverage for loss or theft of private keys, cyber-attack or hacking, and other risks associated with holding or trading cryptocurrencies. The goal of crypto insurance is to provide protection for individuals and businesses that own or deal with cryptocurrencies and to mitigate the financial consequences of such risks. The availability and terms of crypto insurance vary depending on the insurance company and the jurisdiction in which the coverage is being purchased.
DeFi insurance applies the same concepts and mechanisms as traditional ones but is decentralized and operates on a network of computers through blockchain technology and smart contracts. DeFi insurance is powered by smart contracts, which are self-executing and automated agreements between parties, all data and transactions are publicly available and transparent, also keeping lower costs due to its decentralized nature and lack of intermediaries. Moreover, processing times result faster because they are automatically processed, and policyholders can earn interest on their premiums through yield farming.
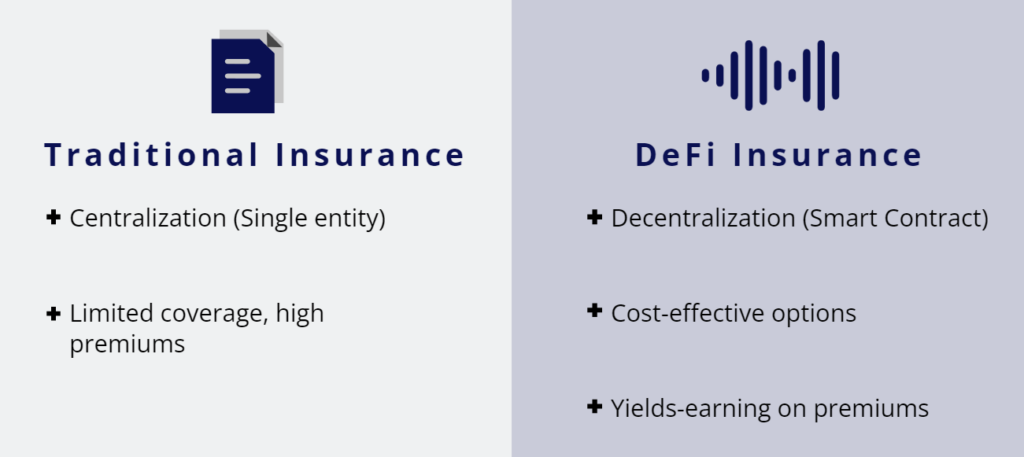
Both traditional and DeFi insurance have advantages and limitations: on one side, traditional insurance offers stability and security, on the other, DeFi insurance offers a more decentralized, transparent, and cost-effective alternative.
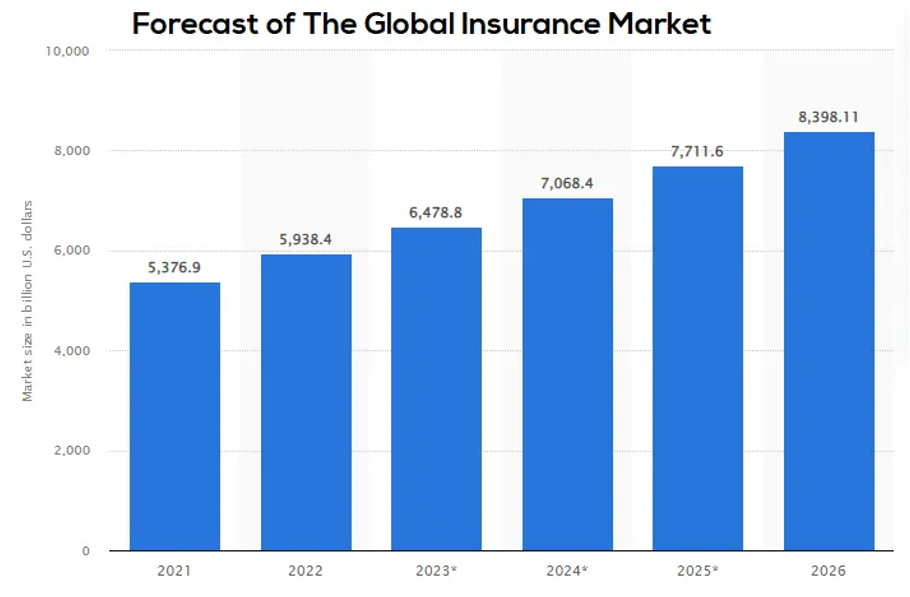
DeFi insurance is still a relatively new and developing area, and there may be a lack of regulation and security concerns; as this space continues to grow and evolve, it will be interesting to see how insurance will change and impact the traditional insurance industry. An increasing liquidity flow is expected in 2023 for what concerns crypto insurance and according to Statista, the global insurance market is forecasted to increase in the following years.
Risks covered by Crypto Insurance
Crypto insurance can provide cover for different types of risks; the coverage offered, and terms of the policies may vary depending on the insurance company and the jurisdiction in which the policy is purchased.
- Loss or theft of private keys (use to access and manage cryptocurrency assets).
- Hacking: covers losses resulting from unauthorized access to a cryptocurrency wallet or exchange due to hacking or other types of cyber-attacks.
- Third-party theft: covers losses from theft by a third party, such as an exchange or wallet provider.
- Insolvency of an exchange: if a cryptocurrency exchange becomes insolvent or otherwise unable to return customer funds.
- Market volatility: covers losses resulting from sudden and unexpected changes in the value of cryptocurrencies.
- Business interruption (such as cyber-attack that disrupts operations).
- Regulatory changes: changes in government regulations that affect the cryptocurrency market and bring losses.
Catastrophic events
We refer to catastrophic events in the most extreme and far-reaching cases, which can be mitigated by having crypto insurance, but given their often-unpredictable nature and the huge impact they are difficult to manage, and it is impossible not to be touched by them. The evolution of this branch of insurance will, over time, lead to a better awareness of how to deal with these incidents, also through increased experience in the field.
Here are some examples of these events:
- Hacks and cyber-attacks: hacker attacks leading to the loss of millions of dollars and involving multiple parties.
- Market volatility: sudden and unexpected changes in value can result in significant losses, due to the volatility that can be extreme.
- Insolvency of an exchange: If a cryptocurrency exchange becomes insolvent, customers may be unable to access their funds.
- Regulatory changes: changes in government regulations can highly impact the cryptocurrency market and result in losses. Moreover, the cryptocurrency market is also very sensitive to changes not directly related to the sector.
When a catastrophic event occurs, the insurance company may be required to pay out claims to policyholders. This can have several consequences for the insurance company, depending on the scale of the event and the number of claims being made.
The first impact could be the financial one, which that means, if the number of claims being made exceeds the insurance company’s reserves and ability to pay, the insurance company may become insolvent and unable to pay out all claims. Also, this can lead to reputational damage, making it more difficult to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
Another consequence can be, in some cases, that the insurance company may be subject to increased regulation or scrutiny from government authorities if it is unable to pay out claims.
A possible way of preventing the impossibility of paying the claims is reinsurance, which is when insurance companies purchase reinsurance, which is essentially insurance for insurance companies. If a catastrophic event occurs, the insurance company may make a claim on its reinsurance policy to help cover the cost of paying out claims.
It’s important to note that the financial stability and ability to pay claims of an insurance company can be affected by many factors, including the size and frequency of claims, market conditions, and the company’s overall financial strength. As such, it’s important for policyholders to carefully consider the financial stability of an insurance company before purchasing a policy.
Cryptocurrencies losses in recent history
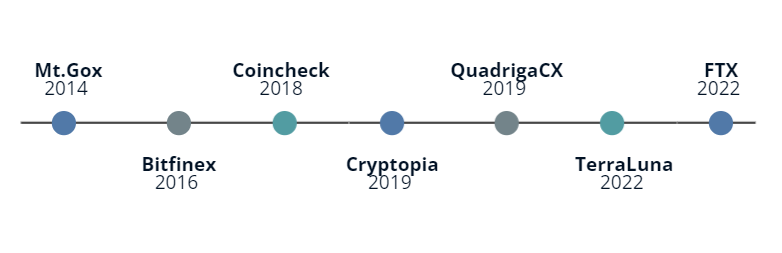
There have been several notable cases of cryptocurrency-related losses in recent history.
- Mt. Gox: Mt. Gox was one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges in the world until 2014 when it filed for bankruptcy after losing 850,000 Bitcoins (worth hundreds of millions of dollars at the time) due to a hack.
- Coincheck: In January 2018, Japanese cryptocurrency exchange Coincheck suffered a hack in which it lost over $500 million worth of NEM tokens.
- Bitfinex: In August 2016, Bitfinex, a Hong Kong-based cryptocurrency exchange, suffered a hack in which it lost 120,000 Bitcoins (worth over $70 million at the time).
- QuadrigaCX: In 2019, Canadian cryptocurrency exchange QuadrigaCX filed for creditor protection after the sudden death of its CEO, who was reportedly the only person with access to the exchange’s cold storage wallets. The exchange claimed to have lost over $135 million in customer funds as a result.
- Cryptopia: New Zealand-based cryptocurrency exchange Cryptopia suffered a hack in January 2019 in which it lost an estimated $16 million in various cryptocurrencies.
- TerraLuna: TerraLuna cryptocurrency token was launched in July 2019 and experienced a strong crash in May ‘22, causing important financial losses. The collapse was mainly due to massive sellouts of its stablecoin sister token Terra Classic USD.
- FTX: the collapse of the cryptocurrency exchange FTX shocked the entire market in November 2022, it took billions of losses and had strong consequences.
Having crypto insurance in place may not guarantee complete protection against all risks and losses, but as said, it can help mitigate the financial consequences of such events.
To wrap up, DeFi insurances are useful, but in case of catastrophes, may not be sufficient. Catastrophic events involving cryptos have an interplanetary character, which an insurance system can hardly handle. In such circumstances, like the most recent FTX one, there is no way to contain the damage. Defi insurance protocols have the property of being very concentrated and targeted at specific risks; although this is a very useful tool, it is only in its early stages and has still to develop.




