Together with…
The Microcredit Industry
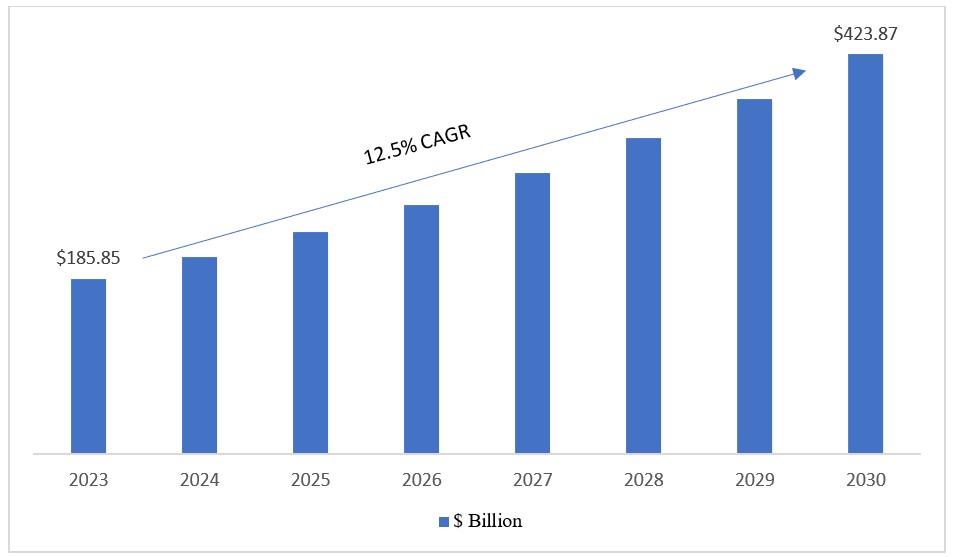
The Microfinance Market size was valued at $185.85 Billion in 2023 and the total Microfinance revenue is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2024 to 2030, reaching nearly $423.87 Billion in 2030. Microfinance is a market providing financial services to low-income individuals or underserved populations, aiming to alleviate poverty and empower them. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) serve as intermediaries, bridging the gap between the formal financial system and individuals excluded due to low income, limited collateral, or remote geographical locations.
Limited access to capital, high costs and interest rates, and limited financial literacy are expected to impede market growth. Borrowers may struggle to understand loan terms, manage their finances effectively, or make informed decisions, leading to over-indebtedness and increased default rates.
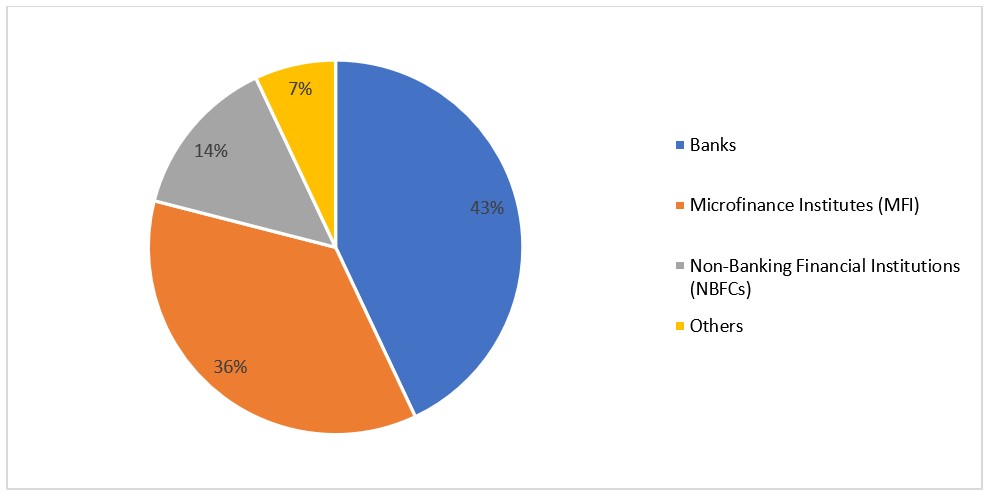
Banks dominate the microfinance market due to their established infrastructure, customer base, and regulatory framework. This enables them to seamlessly offer microfinance services alongside their mainstream banking operations, reaching a diverse clientele.
Technological advancements, such as mobile banking and digital payments, have boosted the demand for microfinance, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and scalable. These digital solutions enable MFIs to reach remote areas with limited traditional banking infrastructure, thereby driving the growth of the microfinance market.
Microfinance institutions offer financial services to aspiring entrepreneurs, enabling them to start or expand businesses. This empowering approach contributes to job creation, income generation, and overall economic development. Microfinance also significantly impacts women’s empowerment, allowing them to overcome traditional barriers and take control of their financial lives. Programs often target women borrowers, recognizing their entrepreneurial potential. Microfinance also promotes gender equality and economic independence. For instance, in April 2023, FINCA Microfinance Bank Limited announced a collaboration with CIRCLE Women, a social enterprise dedicated to women’s economic empowerment and leadership development. The collaboration aims to empower women from low-income strata by promoting digital literacy and financial inclusion under CIRCLE Women’s Digital Literacy Programme (DLP).
As the adoption of entrepreneurship and small business development increases, the demand for microfinance is expected to grow. As a result, individuals are able to build assets, earn regular incomes, and escape poverty. Targeting low-income and marginalized communities, microfinance institutions offer financial services to raise their standards of living and end the cycle of poverty. Moreover, the development of entrepreneurship and small company development is receiving significant investment from governments and industries across the globe, which is expected to propel the expansion of the microfinance industry.
The majority of microfinancing operations occur in developing nations, such as Bangladesh, Cambodia, India, Afghanistan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Indonesia, and Ecuador. The Asia-Pacific region is positioned to emerge as the fastest-growing market for microfinance. This growth is driven by substantial unbanked and underbanked populations, coupled with the recognition of microfinance as a potent tool for uplifting communities.

Small Business Financing
Capital is difficult for small businesses to access for several reasons. Banks want to lend to small companies, but just that traditional banking institutions have outdated, labor-intensive lending procedures and policies that are unfavorable to local shops and small organizations.
The difficulty of accessing capital is exacerbated because many small businesses applying for loans are new and banks typically want to see at least a five-year profile of a healthy business (for instance, five years of tax data) before extending an offer.
CLICK HERE TO GET MORE INFORMATION
Financing Options For Small Businesses
Bank Financing
- Includes term loans, business lines of credit, equipment loans, commercial real estate loans, and business credit cards.
- Requires strong personal credit, established business revenue, and two or more years in operation.
SBA Lenders
- SBA loans offer federal guarantees on loans, making them less risky for banks.
- SBA 7(a) loans, SBA 504 loans, and SBA microloans are popular but require a good credit score, strong annual revenue, and at least two years in business.
Online Loans
- Increased popularity among business owners facing credit challenges.
- Offers fast cash, with some able to approve and fund applications within 24 hours.
- 37% of medium- or high-risk credit applicants applied to online lenders in 2022.
- Offers a variety of small-business financing options, including term loans, lines of credit, and invoice financing.
- Higher borrowing costs with annual percentage rates ranging from 10% to 79%.
Credit Union Financing
- Offers favorable rates and loans backed by the SBA.
- Offers a range of financing options, including lines of credit, traditional term loans, and business credit cards.
Zero-Debt Financing
Small-Business Grants:
- Provides funding for business growth without repayment.
- Typically offered by nonprofits, government agencies, and corporations.
- Ideal for startups and businesses unable to qualify for traditional debt financing.
- Requires extensive application and time investment.
Equity Financing
- Capital received in exchange for business ownership.
- Sources include crowdfunding, venture capital, angel investors, and friends and family.
- Requires product or company to attract multiple investors.
- Strict securities laws and rules apply in equity crowdfunding.
- Worthy for startups but not ideal for long-term financing.
Digital Micro Finance Benefits
- Real-time transaction monitoring and credit history assessment.
- Resolves bookkeeping issues and reduces the need for physical documents.
- Customizes loan offerings based on borrower’s credit history.
- Aids borrowers in digital literacy with local language support and 24/7 chatbot support.
- Addresses long-standing repayment challenges by enabling UPI repayment.
- Mitigates fraud detection using AI/ML and advanced analytics.
- Allows immediate communication of fraud updates and interest rate updates, reducing the time of information dissemination.
Foreign Exchange Risk in Microfinancing and its Implications for Monetary Exchange
Foreign exchange risk is a concern when currency fluctuations affect a company’s competitive position or financial viability. MFIs face this risk when they borrow money in a foreign currency and lend it out in a domestic currency. Some of the risks faced are-
- Devaluation risk arises when they engage in borrowing and lending in foreign currencies. These currency mismatches can significantly affect financial stability due to fluctuations in exchange rates.
- Convertibility risk refers to the possibility that a national government will not sell foreign currency to borrowers or others with obligations denominated in hard currency. MFIs, especially those operating in developing countries, are particularly vulnerable to this risk due to their reliance on foreign currency transactions. Government restrictions on foreign currency outflow can hinder MFIs’ financial obligations and operational sustainability.
- Transfer risk arises when government-imposed restrictions on foreign currency outflow hinder MFIs’ ability to meet their financial obligations. These restrictions can have adverse effects on the operational sustainability of MFIs.
As per the recent survey of MFIs conducted by the Consultative Group to Assist the Poor (CGAP), approximately 50% of MFIs lack sufficient protection against foreign exchange risk. Implementing effective risk management strategies can help mitigate exposure and prevent losses.
When MFIs engage in foreign currency lending, they must adhere to country-specific guidelines. Here’s an illustrative example of the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe’s guidelines –
- Application Process:
- MFIs must submit an application to the Registrar of Microfinance Institutions.
- The application should include evidence of availability and/or capacity to raise foreign currency.
- If the foreign currency was borrowed locally, a copy of the facility letter confirming the source of foreign currency loans should be provided.
- Permissible Sources of Foreign Currency:
- MFIs can access foreign lines of credit with prior approval from Exchange Control.
- Offshore borrowings must comply with current Exchange Control provisions for external borrowing.
- Restrictions on Source of Funding:
- MFIs cannot engage in foreign currency lending without authorization from the Registrar of Microfinance Institutions.
- Cash deposits in foreign currency are subject to a maximum limit of $250. Any approved foreign currency loan amount above $250 shall be disbursed through normal banking channels.
- Borrowers and Loan Agreements:
- MFIs educate borrowers about foreign currency risks.
- Loan agreements for foreign currency-denominated loans should clearly outline terms and conditions, including repayment schedules.
- Administration of Foreign Currency Cash & FCAs:
- MFIs issuing loans in foreign currency must open Nostro Foreign Currency Accounts (FCAs) with Authorized Dealers.
- These FCAs facilitate the banking of foreign currency receipts and disbursements related to loans.
- MFIs must maintain a float of up to USD2,500 to reduce administrative costs.
- Quarterly Reporting:
- Microfinance institutions must submit quarterly reports to the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe or Registrar.
- Reports must detail borrowers, loan purpose, principal amount, installment, and outstanding balance
- Institutions must also report on asset quality for foreign currency loan portfolios quarterly.
Conclusion
The expansion of microcredit programs, alongside technological advancements and innovative financing models, holds promise for advancing financial inclusion and poverty alleviation globally. Microcredit stands as a testament to the transformative power of finance in uplifting communities, promoting entrepreneurship, and driving sustainable development.
While it offers a powerful tool for financial inclusion, there are difficulties with which the system must interface, including currency risk that poses a significant threat to the stability of microfinance institutions (MFIs). Currency, convertibility and transfer risks can erode profits and hamper the ability of MFIs to serve low-income communities. Effective risk management strategies, such as adjusting currency use, hedging with financial instruments and complying with regulations, are critical for MFIs to address these challenges and ensure a sustainable future for financial inclusion and poverty reduction.
Through the principles of empowerment, collaboration and social responsibility, microcredit continues to pave the way towards a more inclusive and equitable future where economic opportunities are accessible to all.
CLICK HERE TO GET MORE INFORMATION
Disclaimer
Index:
Data Room AccessData room access is available only for accredited and institutional investors due to FCA permissions.
To gain access, click and fill out the following form. Our compliance team will grant you access within 24 hours.




