Together with…

Introduction
Staking is a procedure that allows to obtain rewards from the possession of cryptocurrencies by depositing and blocking them in a cryptographic protocol for a certain period of time. It represents a passive investment method, with whom it is possible to earn interest, at a rate calculated on an annual basis and defined as APY (Annual Percentage Yield), and credited on a monthly basis or according to other frequencies defined by the protocol itself. It is an excellent solution to maximize the yield of your crypto funds which otherwise would remain inert on a wallet, awaiting the natural revaluation of the cryptocurrency.
As in the case of mining, staking also performs the important function of transaction verification, control, maintenance and security of the cryptographic protocol. This activity, simpler and more accessible than mining, has turned into an advantageous form of passive income, to be integrated into an investment portfolio as a medium and long-term strategy.
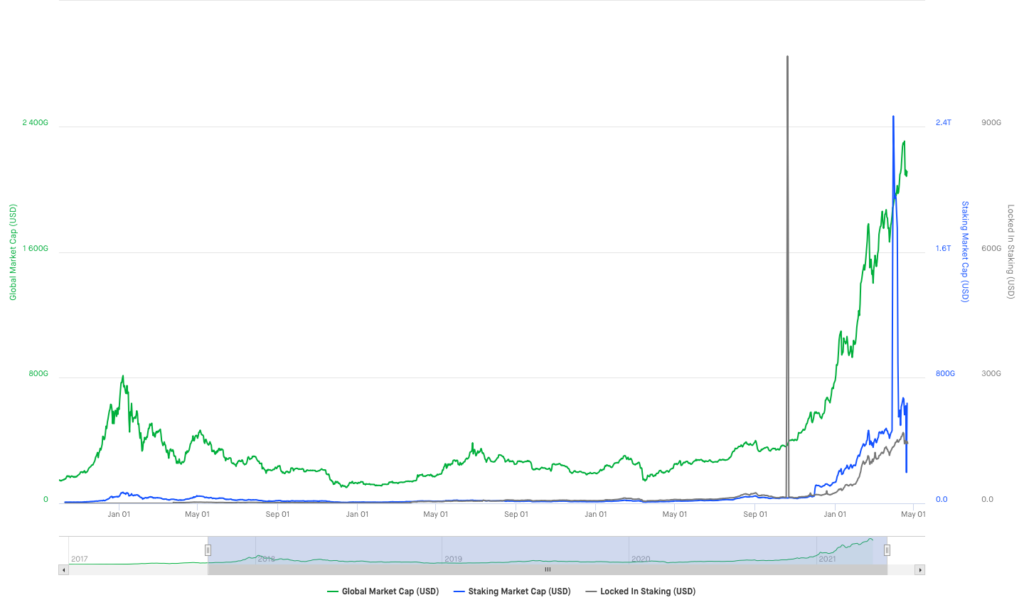
The term “staking” derives from a particular algorithm called Proof of Stake (PoS), and represents an alternative to the more well-known Proof of Work (the classic algorithm underlying traditional mining). Thanks to greater efficiency and less use of energy resources, several major protocols, such as Ethereum, are migrating from PoW to PoS. As evidence of the great interest aroused by this technology, since 2021 we are experiencing the explosion of staking, as shown in the graph below:
Source: Staking Rewards
As shown in the figure above, the total capitalization of staking (blue line), representing the number of resources in millions of dollars blocked in PoS protocols, became relevant from the end of 2020, spreading in a very short time, so much so that in March 2021 it was able to overcome the capitalization of the entire cryptocurrencies market. As of July 2022, a quantity of tokens for a total value of USD 120 billion were deposited in staking protocols.
Focus on APY
APY refers to the acronym of Annual Percentage Yield (annual percentage rate) representing the compound annual interest, generally calculated on a daily basis, and received by those who dedicate their capital in crypto for staking activities. All the platforms that offer the staking service guarantee an APY recognized in cryptocurrency. The yield defined by the APYs is not fixed, but fluctuates over time and is dependent on the law of supply and demand of the cryptocurrencies involved in the staking activity itself.
Proof of Staking and Staking
As defined in the previous analyses, each cryptocurrency operates on its own blockchain, based on algorithms defined as “consensus” which aim to keep the entire network efficient and safe, ensuring its proper functioning.
There are two main types of consensus algorithms:
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS).
Staking is possible on blockchains based on the PoS algorithm. Given the efficiency of PoS algorithms, in recent times, many cryptocurrencies based on PoW algorithms have planned important network updates in order to migrate to PoS models. This is also due to the greater accessibility and lower need for IT and energy resources for users who want to participate in the block validation processes, contributing to the maintenance of the blockchain and earning the related rewards in the form of APY (annual return deriving from the PoS).
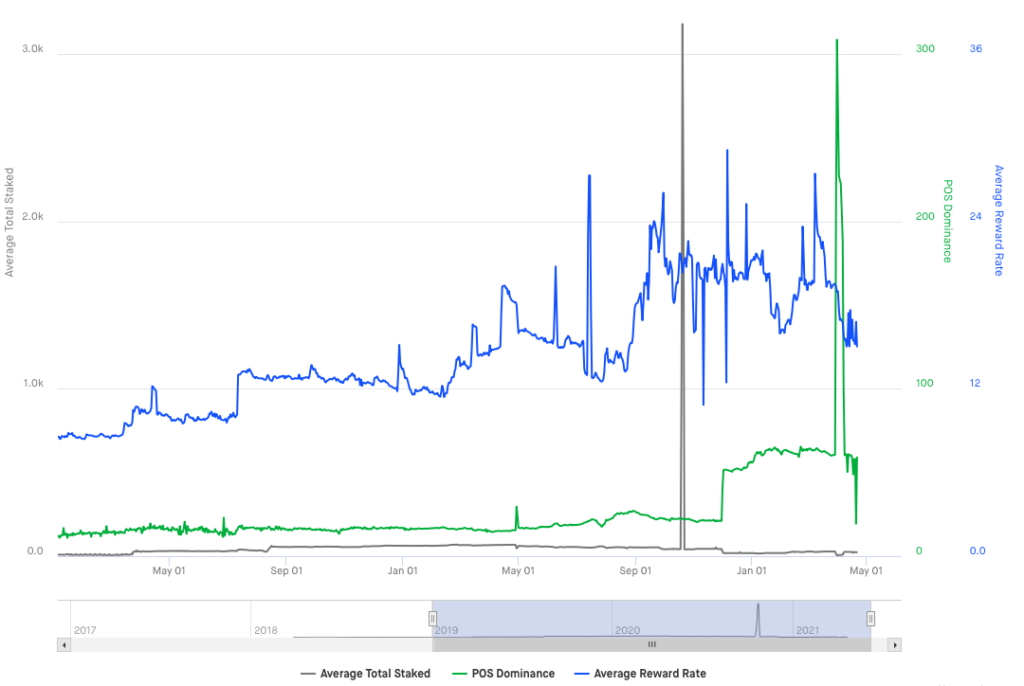
This has generated a proliferation of services that can be used for staking activities, starting from the second half of 2020 these types of networks have become increasingly widespread, reaching 58% of the total cryptographic protocols on the market. It is also interesting to note how the reward rate, or the percentage received on the deposit of tokens, the APYs, is currently in the 8-15% range.
Source: Staking Rewards
Staking therefore consists in the deposit of tokens of a specific decentralized protocol in order to receive rewards and participate, if appropriate requirements are met, in the validation of the blocks of the blockchain. The possibility of performing the function of the validator and therefore accessing larger rewards is defined case by case by the rules of the protocol itself. Generally speaking, we can say that one of the minimum requirements is the deposit of a relatively large cryptocurrency stake.
Regarding the rewards, they can vary depending on several factors, including:
- the total amount of tokens in staking;
- the length of the staking period;
- the total supply of the protocol on which the staking is carried out;
- the inflation rate of staking cryptocurrencies.
However, in order to evaluate the convenience of the staking activity, it is necessary to consider not only the annual interest recognized, but also the price of the token that has been decided to block within the protocol. If, for example, the value of the cryptocurrency in our possession drops significantly during the staking period, it is clear that the gain accrued through interest would be partially or totally eroded by the loss of value of the cryptographic asset, at the time of the conversion of its tokens in FIAT currency.
Staking: benefits and risks
Staking has several advantages, including:
- the ability to capitalize on their cryptocurrency deposits through a passive income with relative ease of use of the service, simply by depositing their tokens, they receiving annual A.P.Y rewards;
- the possibility of participating in the management of the network by applying as validators.
In essence, this activity allows you to capitalize on unused amounts of capital held in cryptocurrency, actively participating in the control, maintenance and security of the entire underlying blockchain.
As with any other type of activity, staking also presents various risks that we need to understand and consider:
- Market risk: in the event of a drop in the prices of the cryptocurrencies locked in staking, the investor could be subject to a more or less substantial loss.
- Liquidity Risk: Staking rewards are guaranteed in the form of cryptocurrencies, so you may have difficulty converting these tokens into fiat money.
- Blocking periods: some platforms impose “lockup periods” in which it is not possible to access the quantity of tokens deposited in staking. In this case, if the price of the asset being staking dropped significantly, you would not be able to withdraw your tokens.
- Risks and costs of validation: actively participating as a validator node, involves costs and responsibilities, and requires compliance with the rules of the protocol which, in case they are broken, can lead to the payment of various penalties, up to the loss of the entire token asset deposited in staking.
- Loss or theft: finally, there is always the typical risk of cryptographic assets, that is, the loss of private keys for accessing the wallet, or the risk of cyber-attacks.
Stake or not to stake
If you have cryptocurrency capital and have no intention of using it for trading activities or converting it into FIAT currency, then staking is an exceptional investment tool, it does not require special technical skills or knowledge of trading strategies, and offers a passive income accessible for every type of user.
However, precisely because of this characteristic intrinsically connected with a “buy and hold” strategy, it makes sense to “buy and stake” only those cryptocurrencies that you are willing to hold for a long time, in which you intend to invest with a medium-term approach, based on a consolidated project with interesting growth potential over time.
Among the cryptocurrencies with the highest market cap, for which staking programs can be activated, the following are worth noting:
Ethereum: the most known smart contract platform on the market. The protocol allows to issue tokens and program decentralized applications called Dapps. On August 5, 2021, the EIP 1559 update (Ethereum Improvement Proposal) was introduced, in order to make the protocol more efficient and start a process to reduce the platform fees. A very important evolution of the protocol is currently underway which will aim to radically change the consensus mechanism from Proof of Work to Proof to Stake. The consequences will be revolutionary: in fact, the issue of new ETH will no longer take place through the traditional mining process using GPUs but through a stacking mechanism: it will be necessary to have a minimum amount of 32 ETH in order to mine new ETH tokens.
Polkadot: created in 2017/18 by the Swiss Web3 foundation, which aims at the total decentralization of the Internet, uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) system. In particular, Polkadot uses the Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS), a new version of PoS in which it is possible to prevent the formation of groups of preferential validators that have a greater number of DOTs staked or that are designated by other users, through a filtering algorithm that equally divides the votes to be awarded.
Kusama: it was founded in 2016 and is a pre-production project for Polkadot, i.e. it allows you to test a new blockchain or application before being made public on the Polkadot blockchain. In fact, even the Polkadot updates are first tested on Kusama and then released publicly, this leads the two blockchains (Polkadot and Kusama) to be very similar in their design. Also, to allow new developers a smoother and more flexible approach, Kusama is governed by far fewer governance rules than Polkadot. Kusama uses two types of blockchains: the main network which takes the name of relay chain, where transactions are permanent and are not eliminated, and user-generated networks called parachains. Finally, as described earlier for the Polkadot blockchain, the Kusama Relay Chain uses a variant of Proof of Stake (PoS) which is commonly referred to as Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS).
In conclusion, staking represents only one of the main services in the DeFi landscape capable of providing passive income to investors, a single piece of an economy in absolute growth and expansion that involves many other services that we will investigate in the next papers.




